There are several types of video editing in the industry of today. In this blog, I will be talking about offline video editing and real-time video editing. How are these two types of video editing different? How are they used in the industry?
Offline Video Editing
Offline video editing is used to eliminate to lag caused high-quality footage when editing in Premiere or After Effects. This is done by compressing the videos to a lower resolution to make it easier for the computer to handle. Once the editing is done, the low-resolution footage is replaced with the raw footage and viola, efficiency over 9000!
This type of editing was used since the good ol’ days with film! As time passed, offline editing became popular because it was easier with the technology they had at the time. However, nowadays people do not often work ‘offline’. Technology greatly advanced over time, it is only used if the computer is not capable to handle raw footage.
In the industry, offline video editing is rarely used unless necessary. Due to advanced computer technology, offline editing is not necessary. However, it may possibly be used when raw footage is in 4K resolution.
Real-Time Video Editing
Real-time video editing is more common in the industry such as sports, music, and events. The best way to do this is with multiple cameras, to get the best shot of whatever it may be they are filming. For sports like hockey, multiple cameras are required to get the best quality. Still-shots work better for events like a piano concert and would only require one camera.
This type of video editing requires multiple CPU’s (computer processing unit), multiple gigabytes of RAM (random access memory) and high-powered hard drives. It is typically only professionally practiced. I believe it is very challenging because there is only one chance to get it right. However, to be efficient, camera work would be practiced to be precise and smooth.
How does this apply to me?
Personally, I will probably not use either form of video editing. This is because my computer has the power to render raw footage and I do not wish to pursue to be in the industry of live TV broadcasting. However, this is new knowledge to me and will one day serve to help me when I have a terrible computer or when I work with super duper high resolution! Thank you for reading my blog, and as always… let’s get this bread.
Photo by Jakob Owens on Unsplash
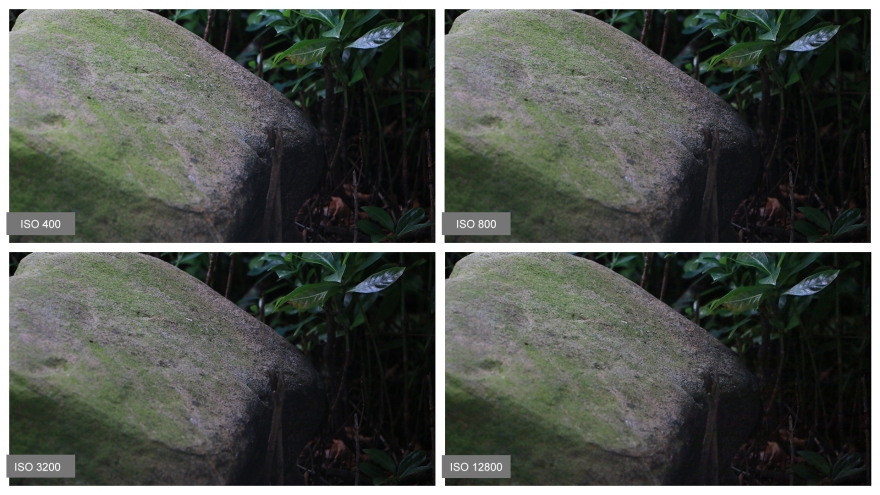
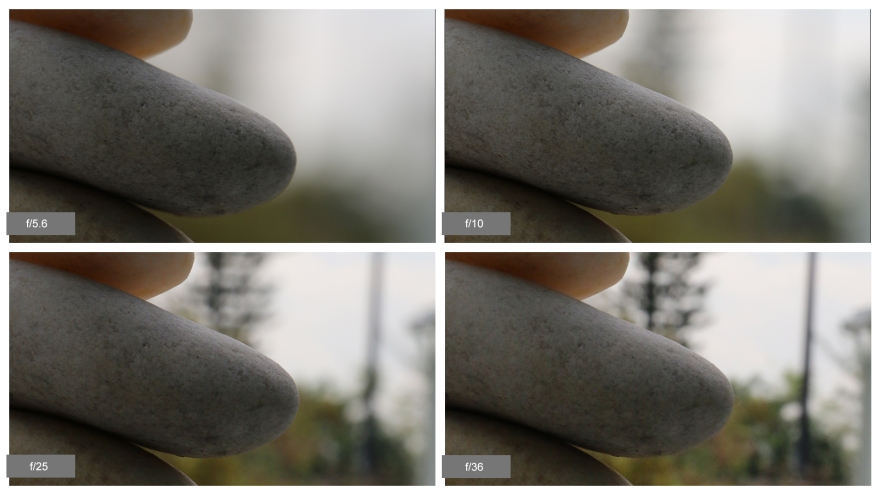
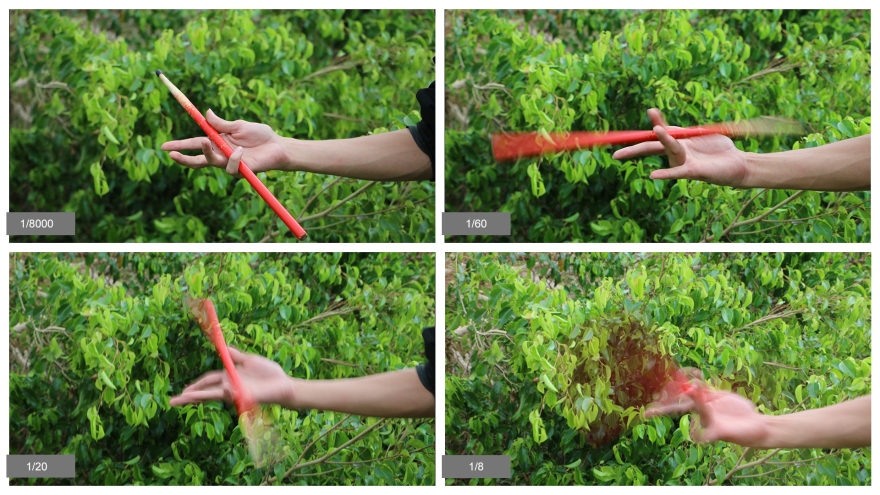


 Using a shutter speed of 1/60 is recommended unless you are using a tripod. Otherwise, camera shake will ruin almost every shot because we are humans and cannot keep a camera still for more than one sixtieth of a second. Be creative when using slow shutter speed to an advantage to showcase things like waterfalls, and the zoomiest cars.
Using a shutter speed of 1/60 is recommended unless you are using a tripod. Otherwise, camera shake will ruin almost every shot because we are humans and cannot keep a camera still for more than one sixtieth of a second. Be creative when using slow shutter speed to an advantage to showcase things like waterfalls, and the zoomiest cars.